Accountability Within An Organisation
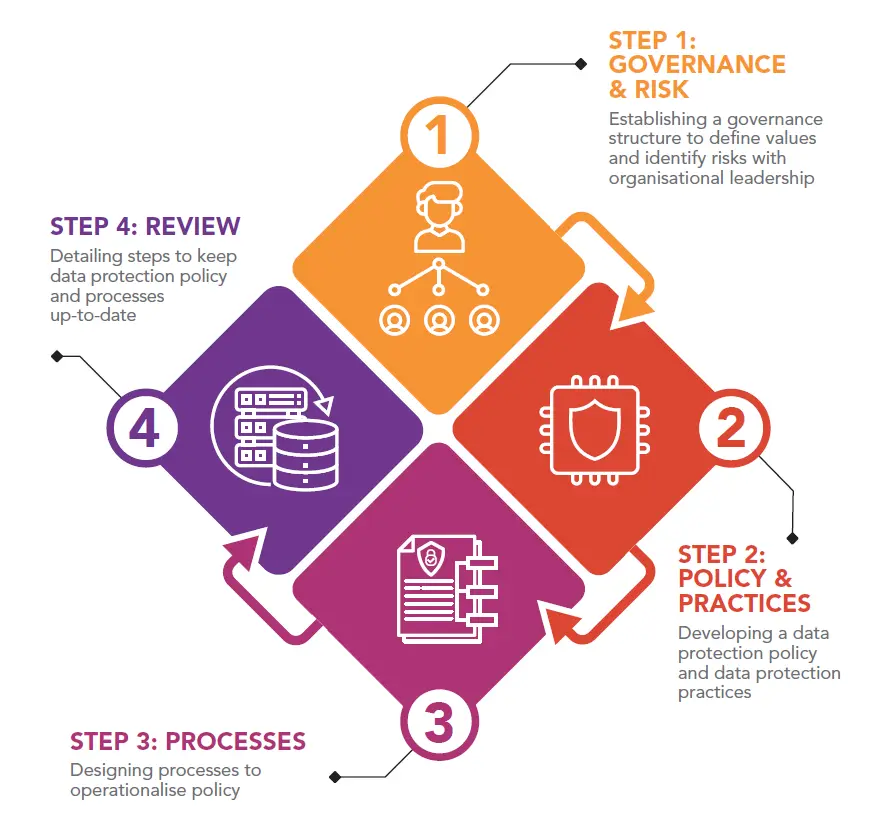
4 Steps of Accountability
While there are mandatory accountability requirements under the PDPA, organisations should consider accountability measures beyond merely complying with the law.
As a good practice, organisations could demonstrate accountability by establishing a structure for governance and risks assessments, by developing management policies and practices for the handling of personal data, and by establishing processes to operationalise them
 |
Step 1: Governance and Risk Assessment |
Good accountability practices begin with an organisation’s leadership, and is directed through its corporate governance. The senior management of an organisation should have an understanding of risks and review the risks on a regular basis to take into consideration changes in business models, regulations, technology and other factors. Thus, a key step to ensure a commitment to accountability is to embed personal data protection into corporate governance.
 |
Step 2: Policies and Practices |
In particular, personal data protection is the responsibility of every employee. It cuts across roles, functions and hierarchy and should be practised by staff (including volunteers and contract staff) at all levels of the organisation as well as third-party service providers.
Having dedicated internal policies and practices on specific areas will also provide clarity to internal stakeholders on the responsibilities and processes on handling personal data in their day-to-day work.
 |
Step 3: Processes |
To set up specific processes, an organisation should begin by documenting its personal data flows to understand how personal data is being collected, stored, used, disclosed and archived/disposed. Thereafter, it should identify key gaps and areas for improvement with respect to data protection, before incorporating data protection practices into business processes, systems products or services.
 |
Step 4: Review |
Find out how to implement these 4 steps in our Guide to Developing a Data Protection Management Programme.
Resources
- Guides
- Data Protection Notice Generator
- EDMs/Posters
- Advisory Guidelines on Key Concepts in the PDPA
- Guides
- Guide on Data Protection Clauses for Agreements Relating to the Processing of Personal Data
- Guide to Notification
- Guide to Data Protection Practices for ICT Systems
- Guide to Preventing Accidental Disclosure When Processing and Sending Personal Data
- Guide to Managing Data Intermediaries
- Board Risk Committee (BRC) Guide by the Singapore Institute of Directors (SID)
- Sample Clauses and Templates
|
|
